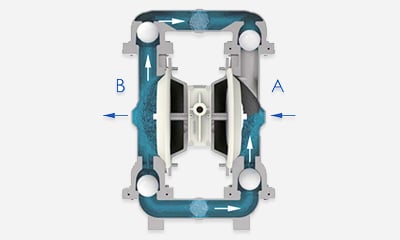
What Is A Diaphragm Pump?
Air operated double diaphragm pump, also known as an AODD pump, Membrane pump, Pneumatic diaphragm pump is a positive displacement pump that uses compressed air as its power source. Compressed air is transferred from one chamber to another by a connected shaft, allowing the chambers to move simultaneously. This back-and-forth movement forces liquid from one chamber into the discharge pipe while the other chamber is filled with liquid.
Diaphragm pumps belong to the category of ” positive displacement ” pump, because at a given pump speed, diaphragm pump flow will not work with the pump flow ” head ” ( or pressure ) change too much. Diaphragm pumps can convey low, medium and high viscosity liquids, but also can convey a large solids content of the liquid. They can also handle many corrosive chemicals, such as acid, because they can be constructed with a variety of valve body materials and diaphragms.



How does a Diaphragm Pump Work?
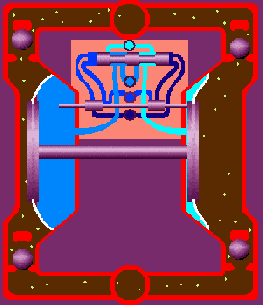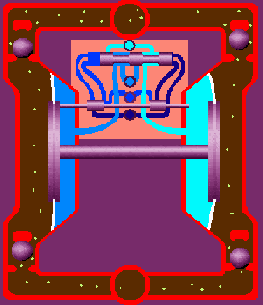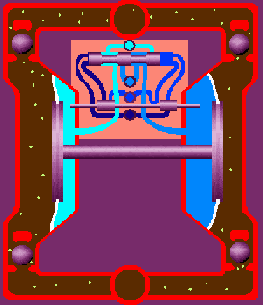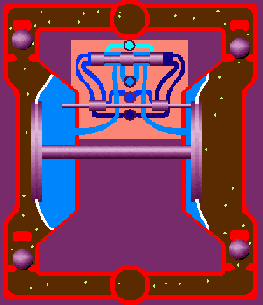
Air double diaphragm pumps utilize two flexible diaphragms that reciprocate back and forth to form a temporary chamber that sucks in and out fluid through the pump. The diaphragms act as a wall of separation between the air and the fluid. The specific operating principle is as follows:
The first stroke
Is through the center section where the air valve is located, with two diaphragms connected by a shaft. The air valve serves to direct compressed air behind diaphragm No.1, away from the center section. The first diaphragm causes a pressure stroke to move the fluid out of the pump. At the same time, diaphragm No.2 is undergoing a suction stroke. The air behind diaphragm No.2 is pushed into the atmosphere, causing atmospheric pressure to push the fluid to the suction side. The suction ball valve is pushed off its seat, allowing fluid to flow through it into the liquid chamber.
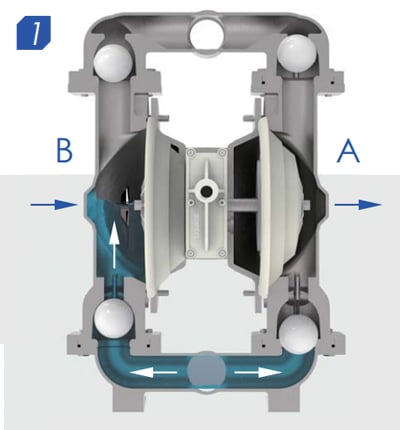
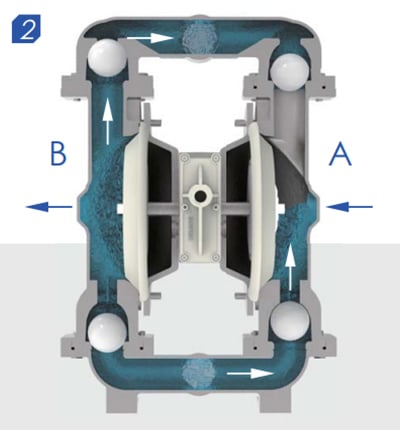
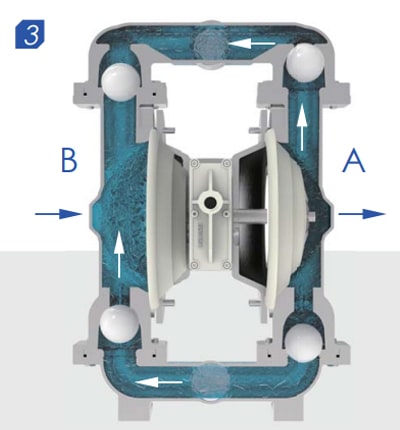
Second stroke
When pressurized diaphragm No.1 reaches the end of its stroke, the movement of air is switched by the air valve from diaphragm No.1 to the back of diaphragm No.2. The compressed air pushes diaphragm No.2 away from the center block, causing diaphragm No.1 to be pulled toward the center block. In pump chamber two, the discharge ball valve is pushed away from the seat, while in pump chamber one, the opposite occurs. After the stroke is complete, the air valve directs the air to the back of diaphragm No.1 again and restarts the cycle.
What Is A Diaphragm Pump Used For?
Conveying fluids:
- Corrosive chemical
- Volatile solvents
- Viscous, sticky fluids
- Shear-sensitive foodstuffs and pharma product
- Dirty water and abrasive slurry
- Smaller solids
- Creams, gels and oils
- Paints
- Varnishes
- Greases
- Adhesives
- Latex
- Titanium dioxide
- Powders

Application scenarios:
- Powder Coating
- General Transfer/Unloading
- Air Spray – Transfer or Supply
- Drum Transfer
- Filter Press
- Pigment Milling
- Paint Filtration
- Filling Machines
- Mixer Tanks
- Waste Water Discharge

Ball Valve Pump VS Flap Valve Pump
Double diaphragm pumps may have ball or disc valves, depending on the type, composition, and behavior of solids in the pumped fluid. These valves operate by utilizing pressure differences in the pumped fluid.
Flap valve is most suitable for large solid (pipe size) or paste containing solids. Ball valves perform best when handling settling, floating or suspended solids.
Another obvious difference between ball valve pumps and flapper pumps is the intake and discharge ports. In ball valve pumps, the suction inlet is located at the bottom of the pump. In flapper pumps, the intake is located at the top, allowing it to handle solids better.
Why Choose An AODD Pump?
Pneumatic diaphragm pump is a versatile mechanical device that enables users to standardize on a single pump type to handle a wide variety of fluids in different industries. As long as there is a compressed air supply, the pump can be installed wherever it is needed, and it can be moved around the plant and easily switched to other operations if conditions change. Whether it is a fluid that needs to be pumped slowly, or a positive displacement AODD pump that is chemically or physically aggressive, it provides an efficient, low maintenance solution.
For Further Questions Please Contact Us
Do you want to know how a pump can help your process control? Leave your contact information and one of our pump experts will get in touch with you!